Medical residency is a crucial phase in the career path of future physicians, providing them with practical experience, refining their clinical skills, and paving the way for specialization in their chosen area of medicine. Through residency or fellowship program that span several years, residents closely collaborate with experienced attending physicians and healthcare teams in diverse clinical settings.
Completion of residency marks a significant milestone, equipping doctors with the expertise and competence required to pursue their desired career paths within various medical specialties, such as internal medicine, pediatrics, surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, psychiatry, radiology, emergency medicine, and more.
Residency programs
Residency programs play a pivotal role in shaping the career path of future physicians. These programs provide a structured curriculum that combines clinical rotations, didactic sessions, and research opportunities. During this period, residents gain invaluable hands-on experience performing medical procedures, making critical clinical decisions, and directly caring for patients.
The residency period is characterized by intense learning, long hours, and significant dedication. Still, it is also a transformative phase where doctors transition from medical students to skilled and confident professionals. By focusing on their chosen specialty, residents receive specialized training that aligns with the specific needs of their field.
They acquire in-depth knowledge and expertise in diagnosing and treating specialized conditions, performing complex surgeries, interpreting advanced diagnostic tests, or providing specialized care to specific patient populations.
Residency also offers a unique environment for professional growth and mentorship. Experienced physicians serve as mentors, guiding residents through the complexities of their specialty and imparting their wisdom and expertise. This mentorship helps shape the future careers of residents and fosters a strong sense of professional development.
Medical residencies play a crucial role in providing comprehensive health services that encompass a broad range of activities promoting, maintaining, and restoring health. As physicians undergo their residencies, they receive extensive training and practical experience in various medical specialties.
Through these residencies, physicians become proficient in delivering preventive care, conducting medical evaluations, performing diagnostic tests, implementing treatment interventions, providing rehabilitation, and offering supportive care.
Additionally, residents have opportunities to engage in research, present their findings at conferences, and contribute to medical literature. These activities allow them to stay updated with the latest advancements in their field, contribute to medical knowledge, and influence the future of medicine. Overall, the residency experience for future physicians is a transformative journey that provides comprehensive training, specialized expertise, and mentorship, paving the way for successful medical careers.

Upon completing their residency program, doctors can apply for board certification in their chosen specialty, further establishing their expertise and credentials. They can then pursue careers as independent practitioners, faculty members at academic institutions, researchers, or even subspecialize through additional fellowship training.
What is a Medical Residency?
A medical residency, or a postgraduate medical training program, is a period of supervised practical training that physicians undergo after graduating from medical school. Residency programs provide hands-on clinical experience for medical students and specialized training in a specific specialty or subspecialty. The primary goal of a residency is to develop and refine the knowledge, skills, and clinical judgment necessary for independent medical practice. Residency training involves a combination of clinical rotations, didactic sessions, conferences, and research opportunities.
What is a Medical Specialty?
Medical specialties are specialized fields of study and practice that allow doctors to delve deeper into specific areas of medicine. These specialties provide in-depth training and expertise, making physicians highly skilled in diagnosing and treating particular conditions. The diverse array of medical specialties ensures that healthcare providers possess the necessary knowledge and skills to address a wide range of medical needs, ultimately improving the overall quality of healthcare. This blog post will explore primary medical specialties, including surgery, internal medicine, pediatrics, psychiatry, neurology, family medicine, pathology, and more.
What are examples of Medical Specialties?
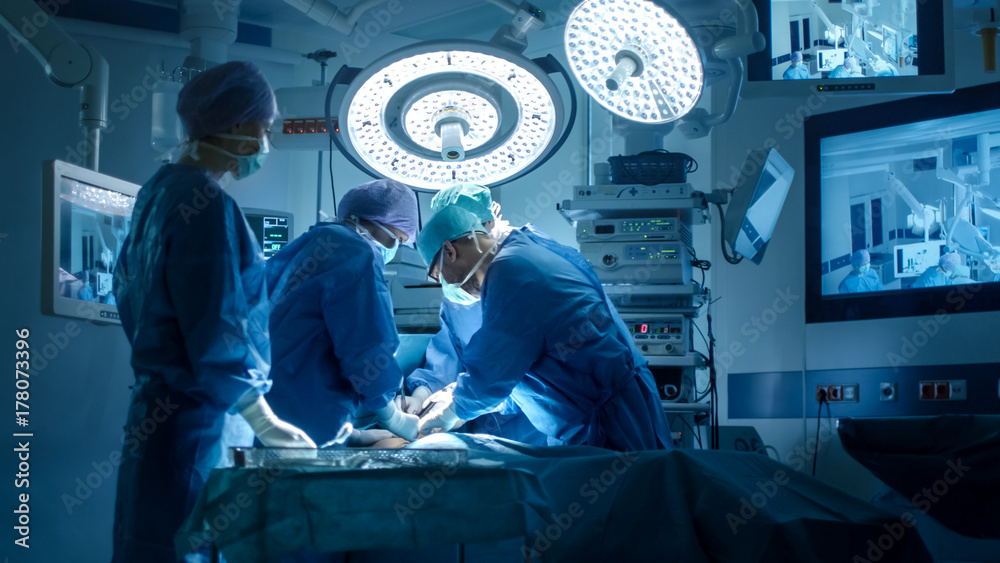
Surgery
Surgery is an exhilarating and hands-on specialty that requires precision, dexterity, and decisiveness. Surgeons specialize in various areas, such as general surgery, orthopedic surgery, cardiovascular surgery, neurosurgery, and more. The field demands critical problem-solving skills, meticulous attention to detail, and the ability to perform under pressure. Surgeons play a vital role in diagnosing, treating, and managing conditions through surgical intervention.
Internal Medicine
Internal medicine focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and non-surgical treatment of diseases in adults. Internists provide comprehensive care, often as primary care physicians or hospital-based specialists. The field encompasses many subspecialties, including cardiology, gastroenterology, nephrology, endocrinology, and infectious diseases. Internal medicine offers a holistic approach to patient care and requires strong diagnostic abilities, critical thinking, and a deep understanding of complex medical conditions.
Physical medicine
Physical medicine is a specialty that focuses on restoring and enhancing functional abilities in individuals with physical impairments or disabilities. Physiatrists utilize a multidisciplinary approach, combining physical therapy, occupational therapy, medication management, and other interventions to optimize physical function, alleviate pain, and improve quality of life.

Pediatrics
Pediatrics is a specialty committed to the health and well-being of infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatricians diligently monitor growth, development, and overall health, diagnosing and treating childhood illnesses with a compassionate and patient-centric approach.
From preventive care to comprehensive treatment, pediatricians play a vital role in promoting children's physical, emotional, and social development, ensuring a healthy foundation for their future. Pediatrics encompasses a wide range of healthcare services, from preventive care to diagnosis and treatment, all dedicated to addressing the unique medical needs of children.
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is a unique specialty that focuses on mental health and psychological disorders. Psychiatrists diagnose and treat conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and addiction. This field demands strong communication and empathy as psychiatrists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans. Psychiatry offers various subspecialties, including child and adolescent psychiatry, geriatric psychiatry, addiction psychiatry, and forensic psychiatry.
Neurology
Neurology deals with diagnosing and treating disorders affecting the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system. Neurologists are critical in managing conditions like epilepsy, stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease. The field requires meticulous observation, analytical thinking, and advanced diagnostic skills. Subspecialties in neurology include neurosurgery, neuropsychiatry, neurocritical care, and clinical neurophysiology.
Neurological surgery
Specialized field that involves the diagnosis, treatment, and surgical management of disorders affecting the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Neurosurgeons undergo extensive training to perform intricate procedures such as brain and spinal tumor removal, cerebrovascular surgeries, and complex spine surgeries to restore neurological function and improve patients' quality of life.
Neuropsychiatry
Subspecialty that combines neurology and psychiatry, focusing on the interface between mental health and brain function. Neuropsychiatrists assess and treat individuals with psychiatric disorders related to neurological conditions, such as epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases.
Family Medicine
Family medicine encompasses comprehensive primary healthcare for individuals of all ages. Family physicians provide preventive care, diagnose and treat acute and chronic illnesses, and coordinate patient care across different specialties. They often act as the first point of contact for patients and offer continuity of care throughout their lifespan.

Pathology
Pathology is disease study through laboratory analysis of tissues, blood, and other bodily fluids. Pathologists play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases and guiding treatment decisions. They collaborate closely with other specialists to analyze samples and provide accurate and timely diagnoses. Pathology offers various subspecialties, including anatomical pathology, clinical pathology, forensic pathology, and hematopathology.
Urology
Urology is a specialty that focuses on diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the urinary tract system in both males and females, as well as the male reproductive system. Urologists are trained to manage conditions like kidney stones, urinary tract infections, prostate issues, and urological cancers, employing surgical and non-surgical interventions to restore urological health.
Gynecology
Gynecology is a specialty that focuses on women's reproductive health, encompassing the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of conditions related to the female reproductive system. Gynecologists care for various issues, including menstrual disorders, infertility, sexually transmitted infections, contraception, and gynecological cancers.
Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology is a specialty that focuses on administering anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety during surgical procedures. Anesthesiologists are skilled in evaluating patients' medical conditions, determining the appropriate type and dosage of anesthesia, and monitoring vital signs throughout the surgical process.

Choosing a medical specialty is a significant decision that will shape your professional life as a physician. In this article, we explore the vast array of medical disciplines available, helping you discover the perfect path for your career.
Understanding the Length, Challenges, and Rewards
Each medical specialty comes with its unique set of challenges, rewards, and opportunities to make a lasting impact on patients' lives. From the demanding and precise practice of surgery to the intricate problem-solving of neurology, this article delves into the majority of challenges faced in different specialties. We also highlight the length of training programs, ensuring you clearly understand the commitment required to pursue your chosen field.
The Role of Fellowships
Beyond residency, fellowships provide further specialized training in specific areas of medicine. This article discusses the purpose and benefits of fellowships, giving insight into how they can enhance your skills and broaden your career prospects. Whether you aspire to be a renowned oncologist or an expert in interventional cardiology, fellowships offer valuable opportunities for professional growth and specialization.
Resources and Support
Embarking on a medical residency or fellowship can be a daunting task, but you don't have to do it alone. We link to Residents Medical, an organization dedicated to helping medical graduates achieve their dream residency or fellowship in the United States. With their guidance and support, you can navigate the application process and increase your chances of success.
Conclusion
In the vast world of medical practice, choosing a specialty is a significant decision. This article serves as a guide to help you discover your passion and align it with your strengths and aspirations. Explore the various options available, consider the challenges and rewards of each specialty, and leverage the resources and support available to you. Remember, your choice of medical specialty will shape your career and allow you to make a meaningful difference in the lives of patients.

